By 2029, the worldwide market for industrial robots is expected to be worth $35.68 billion, up from an estimated $16.78 billion in 2022, growing at a CAGR of 11.4%. Amid this rapid growth, collaborative robots or ‘cobots’ are making a significant mark in various industries, most prominently in manufacturing. They offer unparalleled agility, precision, and efficiency in material handling tasks and revolutionize how they are traditionally performed.
Meanwhile, this article explores the operational mechanics of robotic arms, along with their diverse types and applications, and focuses on the role of cobots in material handling and loading tasks. It underscores the benefits of incorporating cobots into assembly processes and highlights cobots’ advanced AI/ML capabilities, like Techman Robot’s offerings.
How Do Robotic Arms Work?
Robotic arms are intricate machinery created to handle tasks that may be too difficult, hazardous, or monotonous for human workers. They are typically composed of seven metal segments interconnected by six joints. Individual stepper motors control these joints under the regulation of a computer. Unlike regular motors, stepper motors can move in exact increments and allow the computer to execute precise movements repeatedly.
The use of motion sensors ensures that each movement is accurate. Notably, the design of an industrial robotic arm is akin to a human arm, with shoulder, elbow, and wrist-like structures, offering it six degrees of freedom, that is, the ability to pivot in six unique ways.
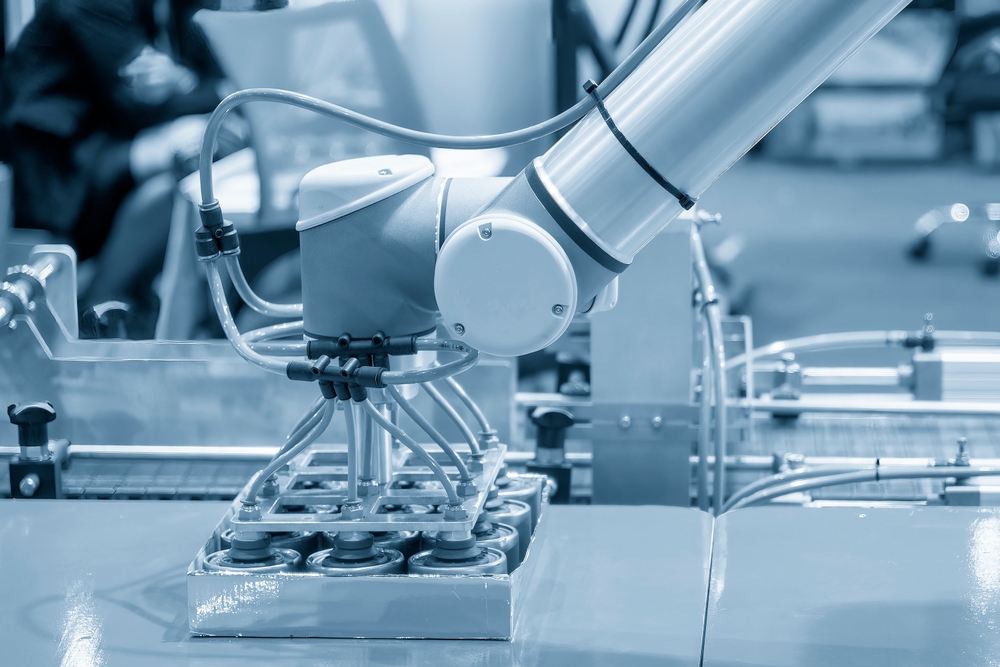
The primary function of a robotic arm is to transport an end effector, equivalent to a human hand, from one location to another. They may include but are not limited to simplified robotic hands, blowtorches, drills, or spray painters. The robotic hand can grasp and transport different objects, with built-in pressure sensors informing the computer about the gripping force. It prevents the robot from dropping or damaging the object it carries.
Industrial robots can memorize a series of steps to accomplish a job after they have been programmed to do so via a portable controller. It allows them to do operations in an assembly line more efficiently, such as capping jars, since they can perform the same action repeatedly.
What Types of Robot Arms Are There?
Let’s discuss the significant types of robotic arms, including the following:
Articulated Robots
Articulated robots, often called anthropomorphic or jointed-arm robots, possess rotary joints varying from two to ten or more interactive joints (axes). They’re designed to replicate the mechanical functionality of complex human arms, thus the term “anthropomorphic.” These robotic arms are incredibly flexible and can maneuver in confined spaces, which is advantageous in various applications. The individual axes in an articulated robot can have different degrees of freedom (DOFs), allowing movements like pitch, yaw, and roll. Such robots are often used in assembly, packaging, material handling, and medical applications.
Cartesian Robots
Cartesian robots (gantry or rectilinear robots) have three linear joints using the Cartesian coordinate system (X, Y, and Z). They offer a box-shaped work envelope and are used in 3D movements like milling and assembling. These robots have the highest level of accuracy and repeatability. Still, they are limited by their inability to reach or around obstacles. They are mountable in any orientation and are typically used in pick-and-place operations, sealant application, assembly operations, and handling machine tools or arc welding equipment.
Cylindrical Robots
Cylindrical robotic arms have at least one rotary joint at the base and one prismatic joint to connect with the links. The rotary joint uses a rotational movement along the joint axis, while the prismatic joint moves linearly. This configuration provides a cylindrical-shaped work envelope. Their construction gives them long, cylindrical workspaces suited for assembly robot arm operations, handling machine tools, spot welding, and diecast operations.
Spherical Robots
Spherical robots, also known as polar robots, are equipped with a twisting joint (rotational) that connects to a link, and two rotary joints connect the links. This type of configuration offers a spherical work envelope, thus the name. These robotic arms can reach into, over, and around obstacles, which provides a wide range of movement. Applications often include handling machine tools, die-casting, fettling machines, gas welding, and arc welding.
V3A076 TM AI Cobot – Welding Solution
What Are Robotic Arms Used for?
The following are the notable applications of robotic arms:
- Manufacturing: Robotic arms are frequently used for complex assembly tasks, with advanced force feedback mechanisms and machine vision capabilities. They also enable automated material handling, palletizing, welding, and painting.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, robotic arms perform minimally invasive surgeries through advancements like the da Vinci Surgical System, which offers surgeon-controlled, high-precision maneuvers. They also automate laboratory processes, including specimen handling, and rehabilitation.
- Agriculture: Robotic arms contribute to harvesting delicate produce with visual recognition and gentle gripping technologies. They also assist in automated planting and pruning while leveraging GPS and sensor data for precision and productivity.
- Space Exploration: Robotic arms in space exploration perform functions like module maneuvering, satellite deployment, and extravehicular support for astronauts. For planetary exploration, they help in sampling and analyzing geological materials.
The utilization of robotic arms, specifically collaborative robots (cobots), exemplifies a paradigm shift in material handling and loading operations. Their deployment is particularly pertinent given their intrinsic ability to supplement human endeavors in tasks characterized by repetitive patterns or necessitating considerable physical strength.
The computational prowess of these cobots, combined with their mechanical dexterity, enables the efficient execution of precise maneuvers. Furthermore, their inherent capability to work in symbiosis with human operators redefines the traditional boundaries of human-robot interaction, effectively leveraging the strengths of both entities.
Why Use Cobots for Material Handling and Loading?
Robotic arms like cobots are beneficial for material handling and loading because they work alongside humans in shared environments. Leveraging advanced sensors and AI algorithms, cobots can execute complex tasks with precision and consistency, which reduces errors and increases efficiency in the supply chain. Plus, their flexible programming and quick setup times allow for seamless integration into diverse workflows, delivering a scalable solution for dynamic manufacturing needs, adaptable to changes in product design or production volume.
For instance, collaborative robots can assist in removing products from an assembly line, applying labels, and packaging them into cartons. They can also help assemble large parts, like automobile doors, by lifting and positioning them onto an unfinished assembly. While such processes may not be suitable for a completely automated operation, a cobot can respond to human operators’ touch and position the part in the desired location.
V2A042 TM AI Cobot – SSD Barcode Inspection
Techman Robot’s AI cobots will help you bring the power of artificial intelligence to your business. Our cobots not only include state-of-the-art AL/ML capabilities, but they also improve over time for you to take advantage of their unrivaled efficiency and adaptability. See how our cobots’ built-in smart vision system excels in various activities, from material handling and AOI inspection to palletizing, and how easy they are to program. Don’t let your business be left behind – optimize your operations today with Techman Robot’s AI cobots.